Every few years, a pre-programmed event ripples through the Litecoin network, slashing mining rewards in half and reshaping the economics of this popular cryptocurrency. Known as “halving,” this mechanism isn’t just a technical footnote,it’s a fundamental pillar of Litecoin’s design, influencing everything from supply dynamics to price speculation and miner behaviour.
For anyone holding, mining, or considering investing in Litecoin (LTC), understanding what halving is and why it happens can be the difference between informed decisions and costly surprises. This event controls inflation, enforces scarcity, and can trigger significant market movements, making it one of the most closely watched dates in the crypto calendar.
In this text, readers will explore the mechanics behind Litecoin halving, its historical impact, what it means for miners and investors, and when the next one is expected. Whether new to cryptocurrency or a seasoned participant, grasping these dynamics is essential for navigating Litecoin’s evolving landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Litecoin halving is a pre-programmed event that cuts mining rewards in half every 840,000 blocks (roughly every four years), directly controlling inflation and enforcing scarcity in the cryptocurrency’s supply.
- The most recent Litecoin halving occurred in August 2023, reducing block rewards from 12.5 LTC to 6.25 LTC, with the next halving expected around mid-2027.
- Litecoin has a fixed supply cap of 84 million LTC, meaning halvings progressively slow new coin issuance until all coins are mined around 2142, creating predictable deflationary pressure.
- Historically, Litecoin experiences price rallies in the months leading up to halving events due to anticipation, but often sees corrections afterward as the news gets priced in.
- Litecoin halving significantly impacts miners by cutting their revenue in half, forcing less efficient operations to shut down while the network adjusts through difficulty mechanisms to maintain security.
- Understanding Litecoin halving is essential for investors because it reduces inflation rates, supports long-term value through scarcity, and creates both opportunities and risks driven by market psychology and speculation.
What Is Litecoin Halving?
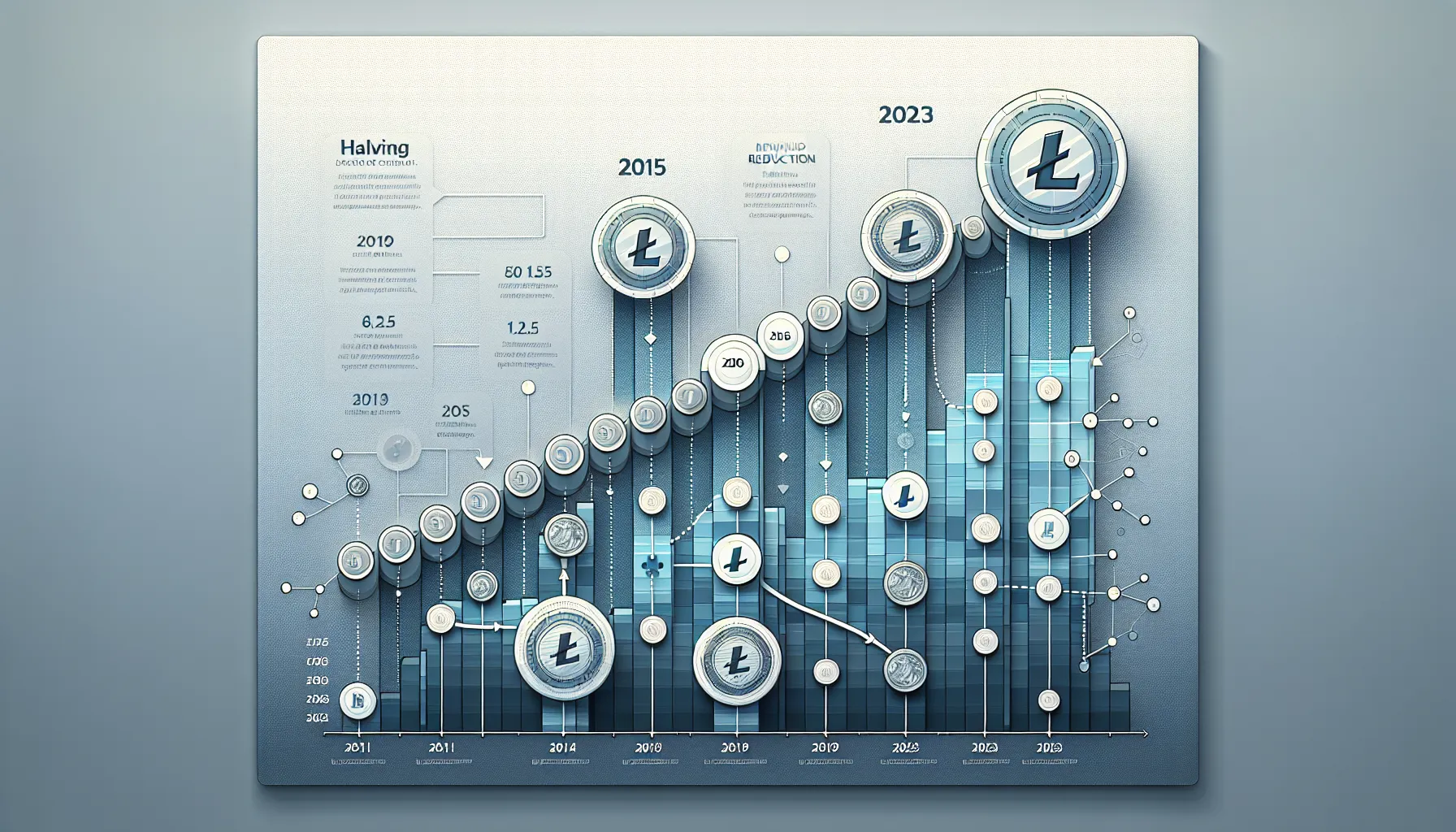
Litecoin halving is a scheduled event written into the cryptocurrency’s code that reduces the block reward miners receive by 50%. In simple terms, every time a halving occurs, the amount of new Litecoin entering circulation through mining is cut in half. This pre-programmed mechanism happens automatically every 840,000 blocks,roughly every four years,and plays a critical role in managing Litecoin’s monetary policy.
When miners successfully add a new block to the Litecoin blockchain, they’re rewarded with a set number of LTC. That reward started at 50 LTC per block when Litecoin launched in 2011. After the first halving in 2015, it dropped to 25 LTC. The second halving in 2019 brought it down to 12.5 LTC, and the most recent halving in August 2023 reduced it further to 6.25 LTC per block.
Understanding Block Rewards and Mining
Block rewards are the backbone of Litecoin’s security and operational integrity. Miners dedicate computational power to solving complex cryptographic puzzles, validating transactions, and adding new blocks to the blockchain. In return, they receive the block reward plus any transaction fees associated with that block.
This incentive structure ensures that miners continue to secure the network even as transaction volumes fluctuate. Initially, when Litecoin was young and transaction fees were minimal, block rewards constituted the vast majority of miner income. As the network matures and halvings reduce these rewards, transaction fees are expected to play an increasingly important role in sustaining mining operations.
Without these rewards, there would be little economic motivation for miners to maintain the infrastructure that keeps Litecoin decentralized and secure. The halving mechanism directly impacts this incentive, making it a central feature of Litecoin’s long-term sustainability.
How the Halving Mechanism Works
The halving process is elegantly simple in execution but profound in impact. Embedded within Litecoin’s code is a rule that triggers automatically after every 840,000 blocks are mined. No human intervention is required,the protocol itself enforces the reduction.
When the blockchain reaches the designated block height, the reward miners receive is immediately cut by half. This reduction doesn’t just slow down the rate at which new Litecoin is created: it also introduces a predictable deflationary pressure into the ecosystem. Because the supply of new coins entering the market decreases while demand can remain constant or grow, the halving has the potential to influence price dynamics.
This mechanism mirrors the supply constraints found in commodities like gold, where scarcity drives value. By systematically reducing the flow of new LTC, Litecoin’s creators ensured that the cryptocurrency wouldn’t suffer from runaway inflation, a problem that plagues many fiat currencies.
Why Litecoin Halving Occurs
The rationale behind Litecoin halving is rooted in economic principles designed to preserve and potentially enhance the cryptocurrency’s value over time. Unlike traditional currencies, which can be printed at will by central banks, Litecoin follows a transparent, immutable monetary policy encoded into its blockchain from day one.
Halving events serve as a built-in brake on inflation. By reducing the rate at which new coins are generated, Litecoin ensures that its supply grows more slowly over time, approaching,but never exceeding,its maximum cap. This predictable scarcity is a core feature that differentiates cryptocurrencies like Litecoin from fiat money, where supply can expand unpredictably based on policy decisions.
Also, halvings create a sense of urgency and anticipation within the market. Investors and traders know these events are coming, and the countdown itself can influence behaviour, driving speculation and attention. The result is a self-reinforcing cycle where scarcity, expectation, and market psychology intersect.
Controlling Supply and Scarcity
Scarcity is one of the oldest drivers of value in economics. From precious metals to rare collectibles, limited supply paired with sustained demand tends to support higher prices. Litecoin’s halving mechanism deliberately engineers this scarcity into its supply schedule.
Every four years, the flow of new LTC slows, making each coin marginally rarer. This controlled reduction mimics the extraction dynamics of gold and silver, where mining becomes progressively harder and more expensive over time. By embedding this characteristic into its code, Litecoin aligns itself with the principles of sound money,money that cannot be debased or inflated arbitrarily.
For long-term holders, this scarcity model offers reassurance. They can be confident that their holdings won’t be diluted by an unexpected surge in supply. For speculators, it provides a predictable catalyst that can drive market interest and volatility.
The Fixed Supply Cap of 84 Million LTC
Litecoin’s monetary policy doesn’t just slow the creation of new coins,it also imposes an absolute ceiling. The total supply of Litecoin is capped at 84 million LTC, exactly four times Bitcoin’s 21 million cap. This hard limit is baked into the protocol and cannot be changed without consensus across the network, a near-impossible feat given the decentralized nature of blockchain governance.
As halvings continue approximately every four years, the pace of new coin issuance slows exponentially. Current projections suggest that the final Litecoin will be mined around the year 2142, over a century from now. By that time, all 84 million LTC will be in circulation, and miners will rely entirely on transaction fees for revenue.
This fixed supply cap is one of Litecoin’s most attractive features for those wary of inflation. It provides a stark contrast to fiat currencies, where central banks can,and often do,increase money supply to meet short-term economic goals, sometimes at the expense of long-term purchasing power.
Historical Litecoin Halving Events
Litecoin has undergone three halvings since its inception, each marking a significant milestone in the cryptocurrency’s evolution. These events offer valuable lessons about market behaviour, miner resilience, and the interplay between supply dynamics and price action.
First Halving (August 2015)
The first Litecoin halving occurred in late August 2015, reducing the block reward from 50 LTC to 25 LTC. At the time, Litecoin was still finding its footing in a crowded and volatile crypto market. Leading up to the event, speculation drove a notable price increase, with traders anticipating reduced supply and potential scarcity effects.
But, the immediate aftermath was less dramatic than many expected. Prices did rise in the months before the halving but experienced correction and consolidation afterward. This pattern,anticipation-driven rallies followed by post-event cooldowns,would become a recurring theme in subsequent halvings.
For miners, the reduction in rewards posed the first real test of Litecoin’s economic model. Some less efficient operations exited, but the network remained secure, demonstrating the resilience of its mining community.
Second Halving (August 2019)
Four years later, in August 2019, Litecoin’s block reward was cut again, this time from 25 LTC to 12.5 LTC. By this point, the crypto market had matured significantly, and awareness of halving events had grown. Media coverage, social media buzz, and investor interest all surged in the months leading up to the event.
Price action mirrored the first halving in some ways. Litecoin experienced a strong rally in the first half of 2019, peaking in June before the August halving. After the event itself, prices declined, disappointing some who had expected the scarcity narrative to drive sustained gains.
Even though the price volatility, the halving reinforced Litecoin’s deflationary model and kept it in the spotlight. Miners adapted once more, with hash rate fluctuations reflecting the new economic realities but eventually stabilizing as the market adjusted.
Third Halving (August 2023)
The most recent halving took place in August 2023, reducing the block reward from 12.5 LTC to 6.25 LTC. This event occurred against a backdrop of broader crypto market recovery following a prolonged bear market in 2022.
Once again, speculation and anticipation built in the months before the halving. Litecoin saw increased trading volume and price movement, though the overall market environment,shaped by macroeconomic factors and regulatory developments,played a significant role in outcomes.
Post-halving, Litecoin’s price exhibited familiar patterns of volatility and consolidation. Miners faced their toughest profitability challenge yet, with rewards now a quarter of what they were at the second halving. Yet the network continued to function smoothly, underscoring the robustness of Litecoin’s infrastructure and the commitment of its mining community.
Impact on Litecoin Price and Market Dynamics
Halvings are often framed as bullish catalysts, but the reality is more nuanced. While reduced supply can theoretically support higher prices, actual market outcomes depend on a complex mix of demand, sentiment, timing, and broader economic conditions.
Price Patterns Before and After Halving
Historically, Litecoin has experienced price rallies in the months leading up to halvings. This pre-event appreciation is driven largely by anticipation,traders and investors buy in early, hoping to capitalize on expected scarcity and media attention. The result is a classic “buy the rumour” dynamic.
But, the period immediately following a halving has often been less favorable. Prices tend to correct or consolidate as the reality of the event sets in and early buyers take profits. This “sell the news” behaviour reflects the fact that markets are forward-looking: by the time the halving actually occurs, much of its impact may already be priced in.
That said, the long-term effects of reduced supply can take months or even years to fully materialize. Some analysts argue that the true price impact of a halving only becomes apparent in subsequent cycles, as the cumulative effect of reduced issuance compounds over time.
It’s also important to note that correlation doesn’t imply causation. While halvings coincide with price movements, other factors,such as Bitcoin’s performance, regulatory news, macroeconomic trends, and technological developments,also play critical roles in shaping Litecoin’s market trajectory.
Market Sentiment and Speculation
Beyond the mechanics of supply and demand, halvings have a psychological dimension. They generate buzz, attract media coverage, and draw attention from both crypto enthusiasts and mainstream audiences. This heightened visibility can lead to increased trading activity and volatility.
Speculation tends to peak in the weeks and months before a halving. Traders attempt to predict price movements, time their entries and exits, and capitalize on short-term swings. Social media platforms, forums, and crypto news outlets amplify the conversation, creating a feedback loop of hype and expectation.
For some, this speculative frenzy presents opportunity: for others, it’s a source of risk. Prices can swing wildly based on sentiment shifts, and not all participants have the risk tolerance or experience to navigate such volatility. Understanding that halvings are as much a psychological event as an economic one is crucial for anyone considering a position around these dates.
Effects on Miners and Network Security
While investors focus on price, miners must grapple with the stark reality of reduced revenues. Halvings cut their income from block rewards in half overnight, fundamentally altering the economics of mining operations.
Reduced Mining Profitability
Mining Litecoin requires significant upfront investment in hardware, electricity, and infrastructure. When block rewards are halved, miners see an immediate 50% drop in one of their primary revenue streams. For operations running on thin margins, this can be the difference between profitability and losses.
Less efficient miners,those with older equipment, higher electricity costs, or smaller economies of scale,are often the first to shut down. This consolidation can shift mining power toward larger, more efficient operations, raising questions about decentralization and network health.
But, miners also earn transaction fees, which can partially offset the loss of block rewards. As Litecoin’s network activity grows and more users transact, fees may become a more substantial portion of miner income. In the long run, the transition from block rewards to fee-based revenue is essential for sustaining the network once all 84 million LTC have been mined.
Hash Rate and Network Security Implications
Hash rate,the total computational power dedicated to mining,serves as a key indicator of network security. A higher hash rate means it’s more difficult for malicious actors to execute attacks such as double-spending or chain reorganization.
Halvings can cause temporary drops in hash rate as unprofitable miners exit the network. This reduction can, in theory, make the network more vulnerable. But, Litecoin has proven resilient across all three halvings to date. While hash rate fluctuations occur, committed miners typically continue operations, and the network adjusts over time.
Litecoin’s difficulty adjustment mechanism also plays a stabilizing role. If hash rate drops significantly, the difficulty of mining adjusts downward, making it easier and more profitable for remaining miners to find blocks. This self-correcting feature helps maintain network stability even as economic conditions shift.
Eventually, the health of Litecoin’s mining ecosystem depends on a balance between profitability, technological efficiency, and the long-term commitment of its participants. Halvings test this balance, but so far, the network has consistently passed the test.
When Is the Next Litecoin Halving?
Following the third halving in August 2023, the next Litecoin halving is expected to occur around mid-2027. This estimate is based on the average block time and the 840,000-block interval between halvings.
When it happens, the block reward will drop from 6.25 LTC to 3.125 LTC, further tightening the flow of new coins into the market. By that point, Litecoin will have been in circulation for over 15 years, and the cumulative effects of previous halvings will have significantly reduced annual issuance.
For those planning to participate in or around the next halving,whether as investors, miners, or simply observers,the lead-up period will likely follow familiar patterns. Anticipation will build, speculation will intensify, and price volatility will increase. But, each halving also occurs in a unique market context, shaped by evolving technology, regulation, and global economic conditions.
Tracking the block height and monitoring countdown timers available on various crypto data platforms can help participants stay informed and prepared. As always, understanding the mechanics and historical precedents provides a foundation for making more informed decisions.
What Litecoin Halving Means for Investors
For investors, Litecoin halving represents both opportunity and risk. The scarcity effect, combined with market psychology, can create conditions for price appreciation. Yet volatility, miner dynamics, and broader market factors mean that outcomes are never guaranteed.
One key takeaway is that halvings reduce the inflation rate of Litecoin. Fewer new coins entering circulation means existing holders experience less dilution, which can support long-term value. This deflationary characteristic is appealing to those seeking an alternative to fiat currencies prone to central bank expansion.
But, investors should also be aware of the speculative nature of pre-halving rallies. Buying at the peak of hype can lead to losses if prices correct after the event. Historical patterns suggest that patience and a longer-term perspective often yield better results than attempting to time short-term swings.
Another consideration is the health of the mining ecosystem. If a halving leads to a significant exodus of miners and a prolonged drop in hash rate, network security could be compromised. While this hasn’t been a major issue in past halvings, it’s a risk worth monitoring.
Diversification, risk management, and staying informed are essential strategies for anyone looking to navigate the halving cycle. Understanding that halvings are just one factor among many influencing Litecoin’s price helps set realistic expectations and avoid hype-driven mistakes.
Conclusion
Litecoin halving is far more than a technical adjustment,it’s a cornerstone of the cryptocurrency’s economic model, designed to enforce scarcity, control inflation, and support long-term value. Every four years, this pre-programmed event reshapes the landscape for miners, investors, and the broader Litecoin community.
Through three halvings, Litecoin has demonstrated resilience and adaptability. Prices have fluctuated, miners have adjusted, and the network has remained secure. Each halving brings its own challenges and opportunities, shaped by the unique conditions of the time.
For those involved in Litecoin,whether holding, mining, or trading,understanding the halving mechanism is essential. It offers insight into supply dynamics, market psychology, and the incentives that keep the network running. As the next halving approaches in 2027, the lessons of the past will inform strategies for the future.
Eventually, Litecoin halving matters because it embodies the principles of sound money: transparency, predictability, and scarcity. In a world where fiat currencies can be manipulated and inflated, these characteristics stand out. And for anyone seeking to understand what makes Litecoin tick, halving is the heartbeat.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Litecoin halving and how does it work?
Litecoin halving is a pre-programmed event that cuts mining rewards by 50% every 840,000 blocks, roughly every four years. This automatic mechanism reduces the flow of new LTC into circulation, controlling inflation and enforcing scarcity within the cryptocurrency’s fixed supply cap of 84 million coins.
When is the next Litecoin halving expected to occur?
The next Litecoin halving is expected around mid-2027, approximately four years after the August 2023 halving. When it occurs, the block reward will decrease from 6.25 LTC to 3.125 LTC, further reducing the rate at which new Litecoin enters circulation.
How does Litecoin halving affect the price of LTC?
Historically, Litecoin experiences price rallies before halvings due to anticipation and speculation, often followed by corrections afterward. While reduced supply can support long-term value, actual price outcomes depend on demand, market sentiment, macroeconomic conditions, and broader crypto market trends.
Why does Litecoin have a halving mechanism?
Litecoin halving controls inflation and creates scarcity by systematically reducing new coin issuance. This transparent, immutable monetary policy mirrors commodities like gold, ensuring Litecoin’s supply grows predictably toward its 84 million cap without arbitrary expansion like fiat currencies.
Can miners still profit after a Litecoin halving event?
Yes, though profitability becomes more challenging. After halving, miners earn 50% less in block rewards but can offset losses through transaction fees. Efficient operations with lower electricity costs typically survive, while less efficient miners may exit the network.
How does Litecoin halving compare to Bitcoin halving?
Both cryptocurrencies use similar halving mechanisms to control supply, but Litecoin halves every 840,000 blocks versus Bitcoin’s 210,000 blocks. Litecoin has an 84 million coin cap—four times Bitcoin’s 21 million—and faster block times, making halvings occur roughly every four years for both.