Moving cryptocurrencies between blockchains isn’t as straightforward as sending money between bank accounts. Different chains don’t naturally communicate, which creates a genuine headache for anyone trying to shift assets from, say, Ethereum to Polygon or Bitcoin to Binance Smart Chain. The good news? Three distinct methods exist to solve this problem: crypto bridges, swaps, and centralised exchange (CEX) transfers. Each has its own strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases.
Understanding which method to use can save you time, money, and, critically, help you avoid security pitfalls that have cost users billions. Whether you’re chasing better staking yields on a Layer 2, diversifying your portfolio, or simply converting crypto to fiat, the choice you make matters. This guide breaks down how each method works, what they cost, and when you should reach for one over the others.
Key Takeaways
- Crypto bridges maintain the same token across blockchains by locking assets on one chain and minting wrapped versions on another, ideal for preserving asset identity.
- Swaps offer the fastest and most cost-effective method for converting one cryptocurrency into another across chains, with minimal custody risk.
- CEX transfers provide simplicity and fiat integration but require trusting a centralised platform with temporary custody of your assets.
- Bridges carry the highest security risk due to complex smart contract interactions, whilst swaps use audited atomic contracts for safer transactions.
- Choosing between crypto bridges vs swaps vs CEX transfers depends on whether you need asset continuity, speed, or fiat accessibility for your specific use case.
Understanding the Three Methods of Moving Crypto
At first glance, all three methods might seem interchangeable, after all, they get your crypto from point A to point B. But the mechanics, outcomes, and trade-offs differ significantly.
Crypto bridges transfer your existing asset across blockchains by locking it on one chain and minting a wrapped version on another. You keep the same token (say, USDC), just on a different network. Swaps, by contrast, convert one cryptocurrency into another entirely, often across chains. You might start with ETH on Ethereum and end up with AVAX on Avalanche. CEX transfers involve sending your crypto to a centralised exchange, trading it there, and withdrawing to your desired network, essentially using the platform as an intermediary.
Each approach involves varying levels of complexity, cost, and security considerations. Bridges require multiple network interactions and smart contract reliance. Swaps leverage decentralised protocols for direct token conversion. CEX transfers hand temporary custody to a third party but offer simplicity and fiat integration. Choosing wisely means understanding not just what each does, but when each shines.
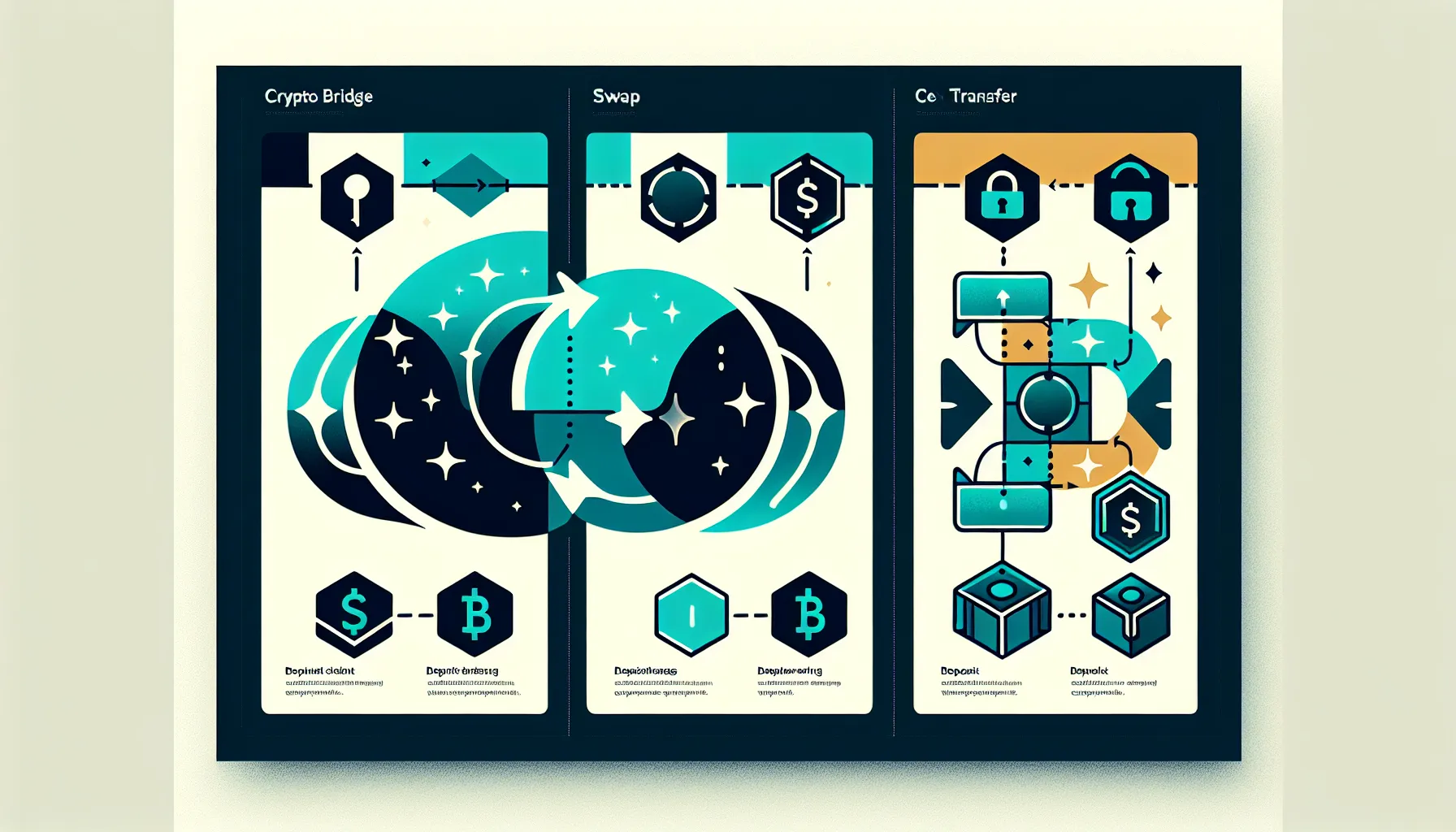
What Are Crypto Bridges?
Crypto bridges are protocols designed to move assets between separate blockchain networks whilst maintaining the token’s identity. Think of them as digital ferries: your ETH boards the boat on Ethereum, crosses to Arbitrum, and disembarks as the same ETH (or a wrapped version like wETH).
How Bridges Work
Bridges operate through a locking and minting mechanism. When you bridge tokens, smart contracts on the source blockchain lock your original assets in a vault. Simultaneously, equivalent wrapped tokens are minted on the destination chain. These wrapped tokens represent a claim on your locked assets, destroy the wrapped version, and you can redeem the original.
This process keeps the underlying value intact. If you bridge 10 USDC from Ethereum to Polygon, you’ll have 10 USDC (or wrapped USDC) on Polygon, backed 1:1 by the locked USDC on Ethereum. The downside? This requires coordination across multiple smart contracts and blockchains, which introduces complexity, time delays, and additional gas fees on both sides of the transaction.
When to Use Bridges
Bridges make sense when you want to maintain exposure to a specific asset whilst accessing opportunities on another network. Perhaps you hold ETH and want to stake it on a Layer 2 with lower fees, or you’ve got USDC and need it on Avalanche for a DeFi protocol offering better yields.
They’re particularly useful for long-term strategies where asset continuity matters, situations where converting to a different token would expose you to unwanted price volatility or tax implications. But, bridges aren’t fast. Transactions can take anywhere from several minutes to hours, depending on network congestion and confirmation requirements. And because you’re interacting with multiple networks, expect higher fees than simpler alternatives.
What Are Crypto Swaps?
Cross-chain swaps take a different approach entirely. Instead of relocating your asset, they exchange it for a different cryptocurrency, often on a different blockchain, in a single trustless transaction. You start with one token and end with another, no wrapped versions, no middlemen.
How Swaps Work
Swaps rely on atomic swap technology and decentralised exchange (DEX) aggregators to find optimal conversion routes. Smart contracts handle the entire process: you deposit Token A on Chain X, and the protocol automatically delivers Token B on Chain Y. Because everything happens through audited smart contracts, there’s no need to trust a centralised party.
DEX aggregators scan multiple liquidity pools and protocols to secure the best exchange rate, minimising slippage and maximising efficiency. The result? A streamlined transaction that’s typically faster and cheaper than bridging. You’re not locking and minting, just converting directly, which reduces the number of blockchain interactions and associated fees.
When to Use Swaps
Swaps excel when speed and cost efficiency matter more than keeping the same asset. If you’re rebalancing your portfolio, trading one cryptocurrency for another, or simply need quick exposure to a token on a different chain, swaps are your best bet.
They’re also ideal when you don’t mind, or actively want, to convert your holdings. For instance, if you’re shifting from BTC to SOL to capitalise on a trading opportunity, a swap gets you there faster and cheaper than bridging BTC, selling it, and buying SOL. The trade-off? You’re subject to market price at the time of conversion, and you won’t have the same token on the other side. But for many use cases, that’s a feature, not a bug.
What Are CEX Transfers?
Centralised exchanges offer a third path: deposit your crypto, trade it on the platform, and withdraw to your desired blockchain. It’s the most familiar method for users who’ve been in crypto for any length of time, and for good reason, it’s straightforward.
How CEX Transfers Work
CEX platforms like Kraken, Coinbase, or Binance locate optimal trading routes across their internal order books and external liquidity partners. When you deposit crypto, the exchange takes custody, meaning they hold your private keys temporarily. You can then trade your asset for another at current market prices and withdraw to whichever blockchain you prefer.
This custodial model simplifies the user experience. You don’t need to worry about gas fees on multiple chains, smart contract interactions, or choosing the right bridge. The exchange handles all the complexity behind the scenes. But, you’re trusting the platform with your assets for the duration of the transaction, and sometimes longer, depending on withdrawal processing times.
When to Use CEX Transfers
CEX transfers shine when you need fiat integration. If you’re in the UK and want to convert GBP to crypto (or vice versa), platforms offering Faster Payments, debit card deposits, or Apple Pay make the process seamless. They’re also useful for users who prefer managed environments with customer support and regulatory oversight.
For straightforward trades between popular cryptocurrencies, CEX platforms offer competitive fees and liquidity. They’re particularly handy when you’re unsure about DeFi protocols or simply want the peace of mind that comes with a regulated entity. The downside? You temporarily surrender control of your private keys, and withdrawal fees can vary significantly depending on the platform and blockchain.
Comparing Costs, Speed, and Security
Choosing between bridges, swaps, and CEX transfers often comes down to how you weigh three factors: cost, speed, and security. Each method makes different trade-offs.
| Feature | Crypto Bridge | Crypto Swap | CEX Transfer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | Slower (minutes to hours) | Faster (seconds to minutes) | Variable |
| Fees | Higher (multiple network interactions) | Lower (single consolidated transaction) | Moderate to low |
| Security Risk | Higher (bridge-specific exploits, complexity) | Minimal (audited smart contracts) | Moderate (custodial risk) |
| Complexity | Complex, multiple steps | Simple, user-friendly | Simple |
| Asset Outcome | Same token, different chain | Different token, same/different chain | Variable |
| Custody | Non-custodial | Non-custodial | Custodial |
Fee Structures Across All Three Methods
Swaps generally offer the most cost-effective solution. By eliminating token-locking mechanisms and reducing blockchain interactions, they keep fees low, often just a single transaction fee plus a small DEX protocol charge. Bridges, on the other hand, require you to pay gas fees on both the source and destination chains, plus any protocol fees for the wrapping and unwrapping process. During periods of network congestion, these costs can add up quickly.
CEX transfers sit somewhere in the middle. Most platforms charge maker/taker fees ranging from 0.02% to 0.26%, depending on your trading volume and the exchange. Withdrawal fees vary by blockchain, sending ETH on Ethereum mainnet will cost significantly more than withdrawing on a Layer 2 or sidechain. Some exchanges also impose minimum withdrawal amounts, which can be inconvenient for smaller transactions.
Security Considerations and Risks
Bridges carry the highest security risk amongst the three methods. The complexity of locking assets on one chain whilst minting them on another creates multiple attack vectors. Bridge exploits have resulted in billions in losses over the past few years, with hackers targeting vulnerabilities in smart contracts or consensus mechanisms. Also, reliance on third-party validators or oracles introduces points of failure.
Swaps mitigate many of these risks through simpler, more audited smart contracts. Since they don’t require asset locking or cross-chain messaging, the attack surface is smaller. Most reputable DEX aggregators have undergone extensive security audits, and because transactions are atomic (they either complete fully or not at all), the risk of partial failure is minimal.
CEX transfers introduce custodial risk. Whilst regulated platforms like Kraken and Coinbase carry out robust security measures, cold storage, insurance policies, regulatory compliance, you’re still trusting a third party with your private keys. Exchange hacks, though less common than in crypto’s early days, remain a real concern. On the flip side, for users uncomfortable with self-custody, a regulated CEX offers protections that decentralised alternatives can’t match.
Which Method Should You Choose?
The right choice depends on your specific needs, priorities, and comfort level with different technologies.
Choose bridges when maintaining the same asset across chains is essential. If you’re moving ETH to a Layer 2 for staking, or transferring USDC to a sidechain for a specific DeFi protocol, bridges preserve your token identity. They’re best suited for longer-term strategies where you plan to hold or use the asset on the destination chain for an extended period, making the higher fees and slower speed worthwhile.
Opt for swaps when you prioritise speed, cost efficiency, and don’t need to keep the same token. Swaps excel at portfolio diversification, quick trades, and situations where converting assets is part of your strategy. They’re also the most user-friendly decentralised option, with minimal custody concerns and streamlined transactions. If you value non-custodial control and want to avoid exchange intermediaries, swaps are your go-to.
Use CEX transfers when you need fiat integration, prefer managed platforms, or want the simplicity of a familiar interface. They’re particularly valuable for UK users accessing GBP deposit methods like Faster Payments or debit cards. CEX platforms also offer robust customer support and regulatory protections, which can be reassuring for less experienced users or larger transactions.
In practice, many crypto users employ all three methods depending on the situation. There’s no universal “best” option, just the right tool for each job.
Conclusion
Bridges, swaps, and CEX transfers each solve different problems in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Bridges maintain asset continuity across blockchains, making them ideal for accessing new networks without converting holdings. Swaps deliver speed and affordability for direct token conversion, with minimal custody risk. CEX transfers provide accessible entry points, fiat integration, and the comfort of regulatory compliance.
Your choice eventually hinges on whether you’re converting assets or preserving them, how much you value speed versus cost, and your tolerance for complexity and security trade-offs. Understanding these distinctions ensures you’re not just moving crypto, you’re doing it efficiently, safely, and in line with your broader strategy. As the blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve, mastering all three methods will only become more valuable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between crypto bridges and swaps?
Crypto bridges transfer the same asset across blockchains by locking it on one chain and minting a wrapped version on another, whilst swaps convert one cryptocurrency into a different token entirely, often across chains, through a single trustless transaction.
Which method is cheapest for transferring crypto between blockchains?
Crypto swaps generally offer the most cost-effective solution, requiring just a single transaction fee plus a small protocol charge. Bridges require gas fees on both source and destination chains, whilst CEX transfers charge trading and withdrawal fees.
Are crypto bridges safe to use?
Crypto bridges carry the highest security risk amongst transfer methods due to their complexity. Bridge exploits have resulted in billions in losses, as they rely on multiple smart contracts and cross-chain messaging that create potential attack vectors.
When should I use a CEX transfer instead of a bridge or swap?
Use CEX transfers when you need fiat integration, prefer managed platforms with customer support, or want regulatory protections. They’re particularly valuable for UK users accessing GBP deposit methods like Faster Payments or debit cards.
How long does a cross-chain crypto swap typically take?
Cross-chain swaps are typically faster than bridges, completing in seconds to minutes. They streamline transactions by converting tokens directly rather than locking and minting, which reduces blockchain interactions and processing time compared to bridge transactions.
Can I lose money using wrapped tokens from crypto bridges?
Wrapped tokens maintain 1:1 backing with locked originals, but you face risks from bridge exploits, smart contract vulnerabilities, and potential de-pegging events. Always verify the bridge’s security audit history and use established protocols with proven track records.